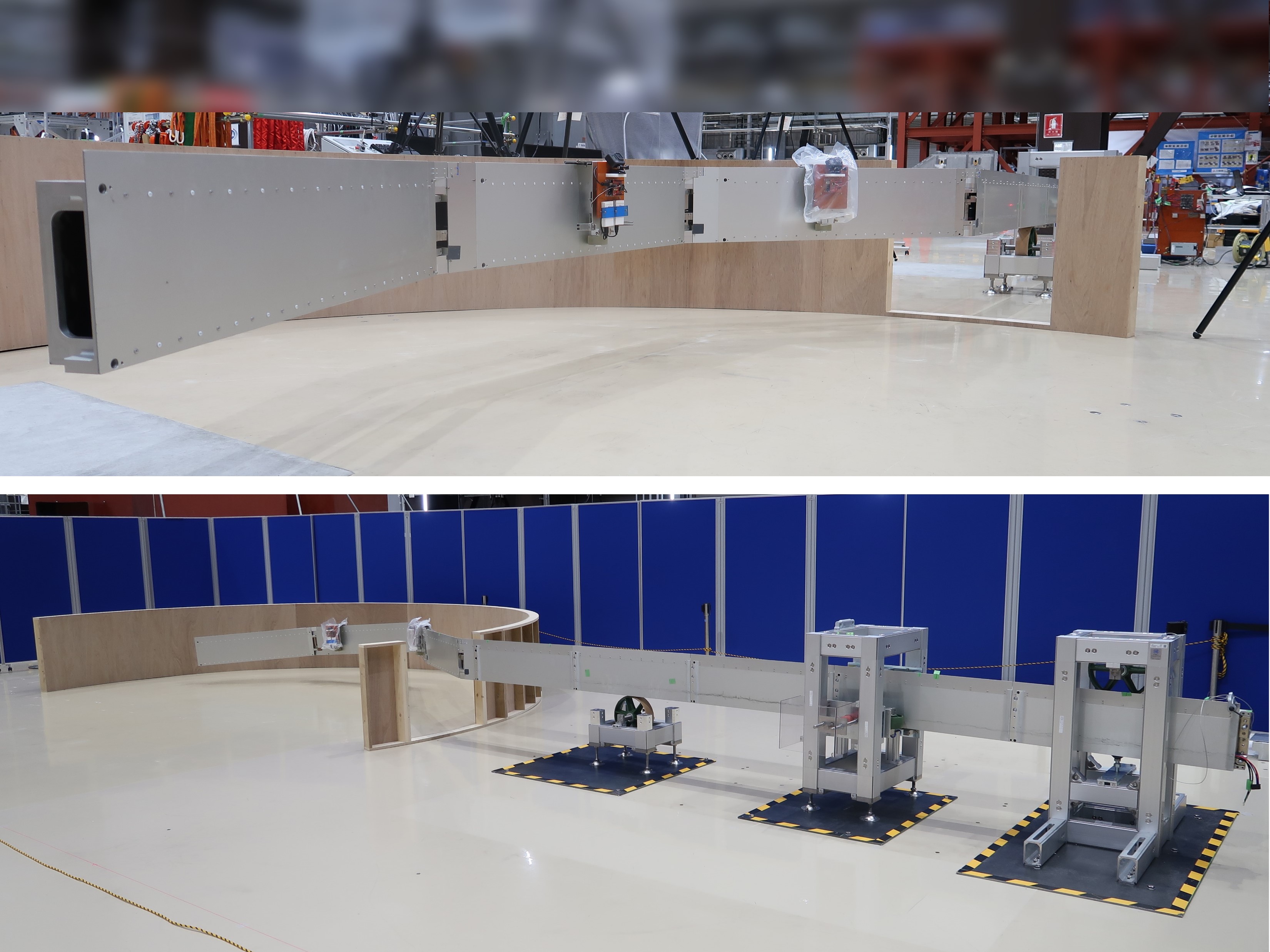
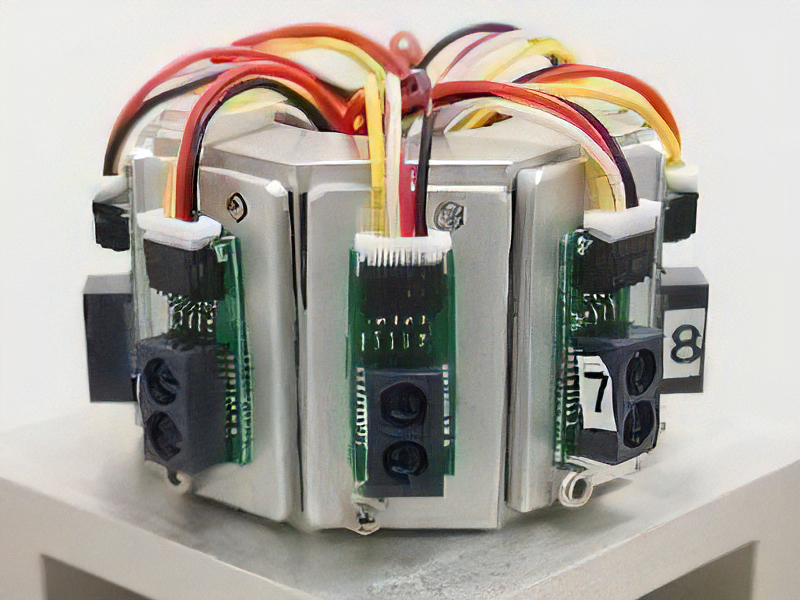
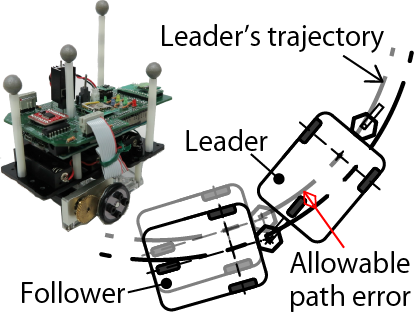
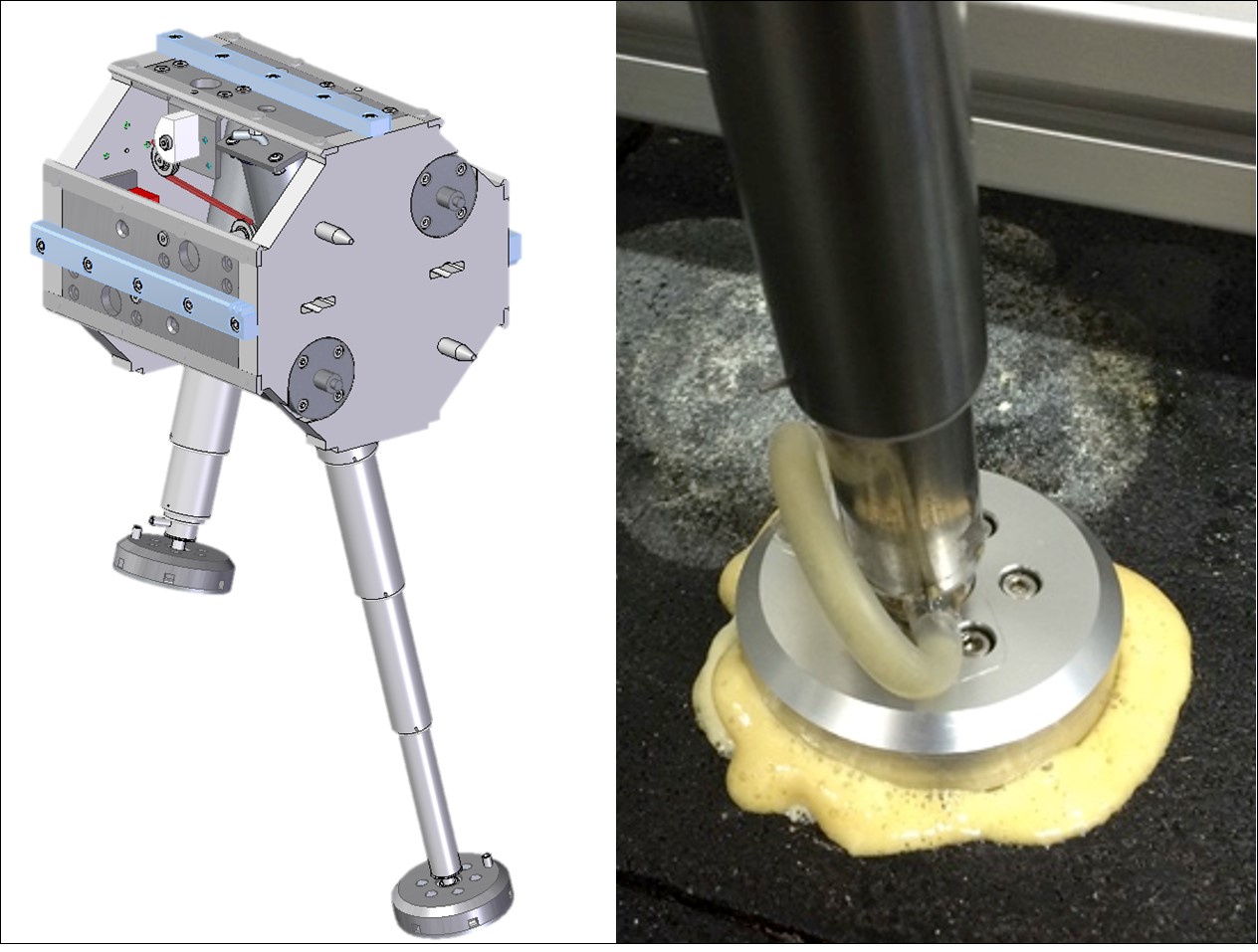
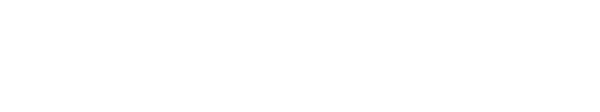Rail Structure Supporting Mechanism using Resin Foam
For hazardous environments, our research group is now developing an automated construction system of robot locomotion and operation whose rail structure is modularized. To realize solid fixation of the rail structure against an environment, a rail structure supporting mechanism is essential. The developed mechanism uses resin foam for three different functions; actuator, adhesive material and structural material. This characteristic realizes quite compact but strong temporal supporting performance.
Functionally distributed machines for underground mining
Recent years, underground mining method is becoming popular because of its potentially high productivity and efficiency. In this method, a mining machinery; load haul dump (LHD), is used as both an excavator and a transporter of ore. Our research group proposes a distributed system that realizes the excavation and transport functions with separated vehicles, an excavator and a transporter. In addition, we proposes a mining map and configurations suitable for the proposed distributed system. To evaluate the productivity of the proposed system, a simulation environment has been developed. Analysis using the simulator reveals what performance factors of the excavator and the transporter have large impacts on the productivity. Simulation results also demonstrate the difference of potential between LHD system and the distributed system that can be explained based on their functions allocation.
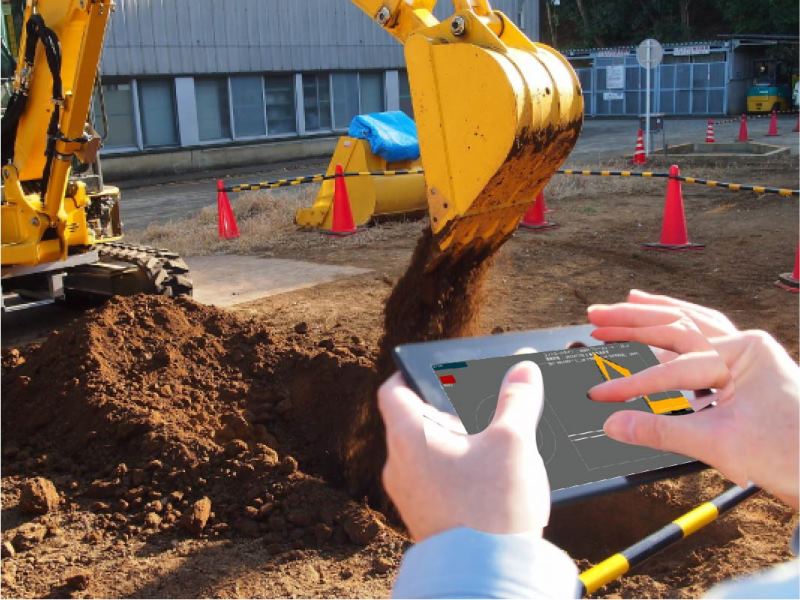
Imitation-based Control of Automated Ore Excavato
Resource exploitation work involves substantial number of dangerous and grueling tasks. Automation of mining machines serves to protect operators from a hazardous environment. This study aims to develop an automation method with high productivity for the fragmented rock pile excavation which is a typical task in resource exploitation. In order to realize a high productive bedrock excavation, the excavator has to change excavating motion according to the change of the rock pile condition. Skilled operators have enough knowledge about the bedrock condition and excavating motions, therefore, they are able to select appropriate excavating motion according to the rock pile condition. This paper proposes an imitation-based autonomous excavation method which includes a rock pile condition recognizer and an excavating motion planner utilizing operators' know-how.
Real-time and Wide-ranging Internal Observation of Diesel Particulate Filter
Particulate Matter (PM) contained in the exhaust gas of Diesel engine has negative effects on the respiratory organs of human body. As a way of reducing the amount of PM contained in the exhaust gas, Diesel Particulate filter (DPF) is widely used. In this research, we have developed a visualization method to realize the real-time and wide-perspective internal observation of DPF. We conducted an observation experiment using a diesel engine and DPF. We have succeeded to acquire internal images of DPF when PM deposit layers have collapsed, channel plugging have happened and so on.
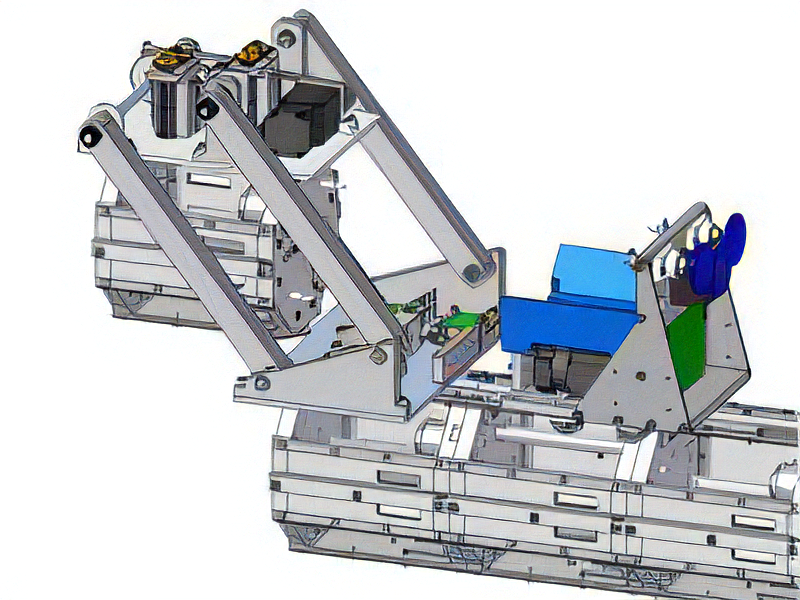
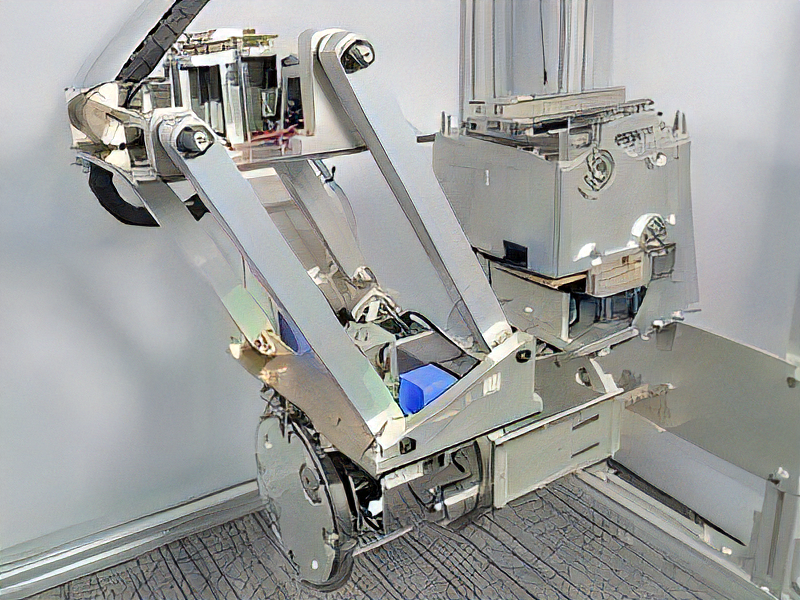
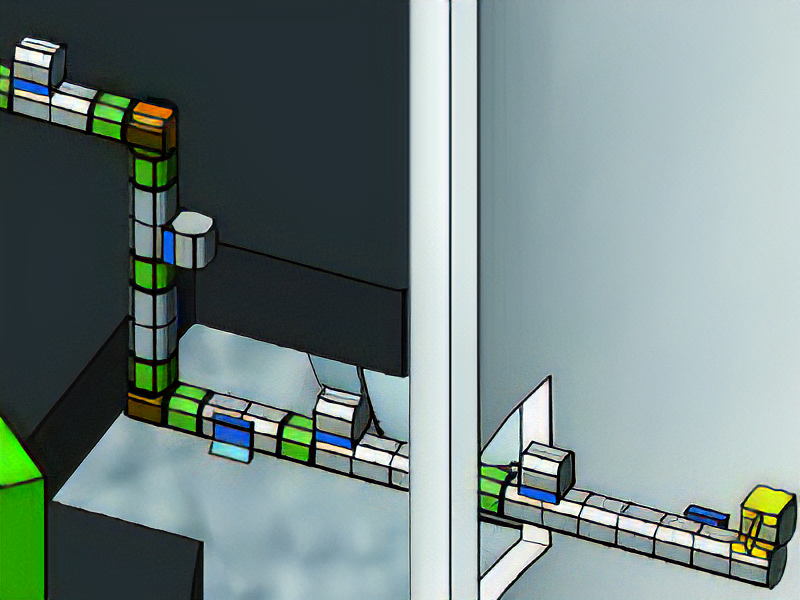
HangBot: a Ceiling Mobile Robot with Robust Locomotion under a Large Payload
This research aims to develop a ceiling mobile robot that can sustain a large payload and can locomote freely under a ceiling space. In our approach, a perforated metal, one of the recent popular architectural materials, is utilized as a ceiling plate and the robot hooks and hangs the sequential holes of the ceiling plate by mechanical constraint. To realize the robot, we developed three key mechanisms, (1) ceiling hanging mechanism for the perforated metal, (2) horizontal locomotion mechanism like an inchworm, and (3) pantograph mechanism for smoothing horizontal locomotion speed and for load balancing. Those basic methodologies of the robot is to be preserved as patents, therefore, we have already applied for PCT. Now we are searching companies that can execute a collaborative research with us.
High Efficient Traction Drive System Using Piezoelectric Actuator
Traction drive is a useful power transmission method for resolving noise problem of electric vehicle. It is composed of pressed two rollers. Oil becomes glassy because the pressure between rollers is high, and the torque is transmitted from input roller to output roller. Its efficiency is lower than gears because of the normal force between rollers. Adjustment of the normal force is necessary to increase the efficiency. In this study, piezoelectric actuator is used for adjusting the normal force. It is an actuator deformed by the voltage, and known for its large force and small displacement. It is undesirable to use piezoelectric actuator with a low rigidity force sensor. Therefore, we developed a normal force control method by sensing the slip between rollers instead of the normal force. Two rollers machine is manufactured to confirm improvement of efficiency using the proposed control method.
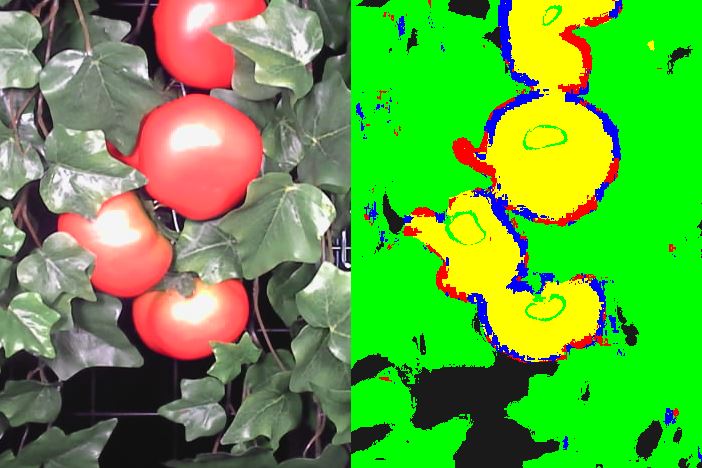
Growth Measurement of Tomato Fruit based on Whole Image Processing
Crop grow measurement technologies are important to increase the farm productivity. Detection and measurement of fruit volume are useful for forecasting and harvesting applications. Some environmental challenges such as lighting conditions or occlusions make the fruit detection difficult. Our approach is based on features extraction from images through a sub-image clustering technique. Then images being described as a number of pixel in various labels are used in a regression model to estimate the fruit volume. The validity of the proposed method in experimental condition is successfully verified. The method is evaluated also in a field condition but results were inferior to the expectation.
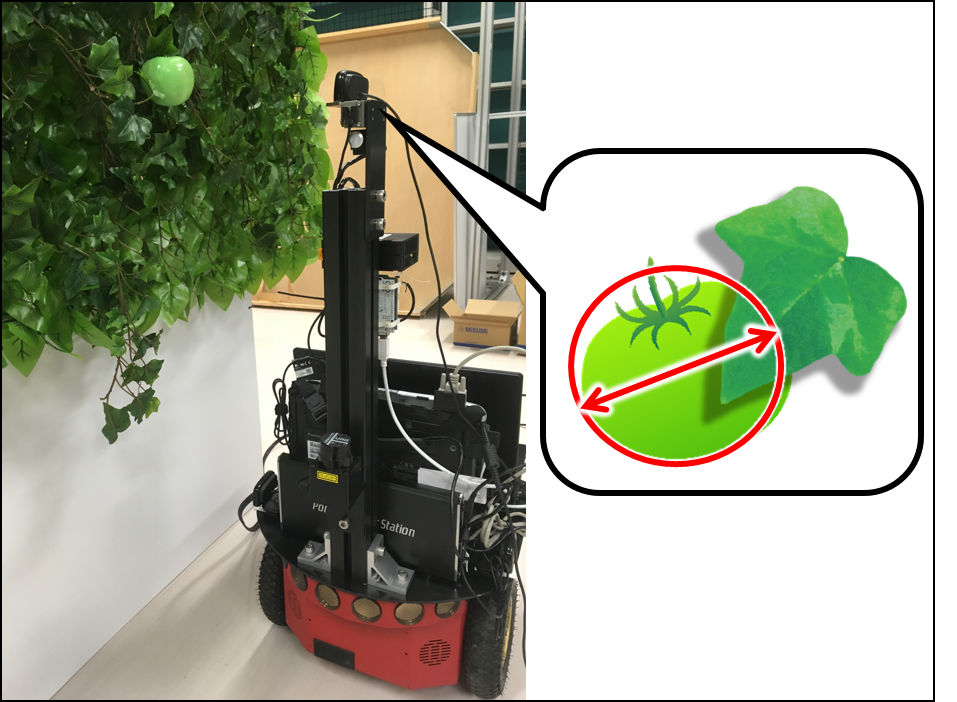
A tomato fruit volume estimating robot
In recent Japanese agriculture, promotion of data mining using knowledge of skilled farmers is getting remarkable. In tomato cultivation, it is important to acquire size data of green immature tomato fruits while they are growing. To achieve the goal, we have developed a tomato monitoring robot that searches autonomously a proper position for observation. The mobile robot patrols around a tomato field and finds out fruits. It generates fruit 3D point cloud using an on-board stereo camera, and estimates fruit width by analyzing point cloud. Furthermore, the estimation result is immediately evaluated to improve the quality of acquired data by rejecting unreliable data and retrying the measurement if necessary.
Daily walking ability assessment system with a distance sensor array
Walking ability has a strong impact on the health of elderly people. However, daily walking ability assessment was difficult because it was measured manually by medical or care staffs in medical facilities or elderly houses. In this work, we propose a system for estimating walking ability that can be easily installed in a home. This system uses multiple inexpensive distance sensors as an array device, which allows to estimate walking speed and step length. We conducted an experiment on 14 elderly people. In the experiment, elderly people walked with speed of 0.48-1.05m/s and step length of 0.29-0.58m. The experimental results show that the Mean Relative Error (MRE) were 6.7% in walking speed and 3.9% in step length. This superior results were realized by our originally developed device and algorithm.
CFloor: An Electrostatic Capacitive Floor Sensor for Human Position Monitoring
We are developing an electrostatic capacitive floor sensor system with low-cost, easy-installation and maintenance-free advantages for monitoring human position in a living space. Features of the sensor system are conciseness that the system is made of very simple parts, that means it is inexpensive, and modularity that enables easy expansion of the sense area. Experiments confirmed the sensor characteristics for human monitoring and showed the feasibility of the accurate sensing with only concise recognition and filtering processes.
Home-use logistical support robot system
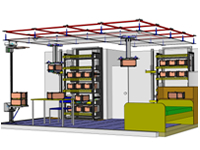
With industrial or economical developments, our living space is being over-flown with too much objects and information. To solve the problem, we present a new living space system: a home-use logistical support robot system, which utilizes IT (Information Technology) and RT (Robot Technology). A core technology of our system is intelligent container (i-Container) which plays a role of logistical mediator between humans and robots. When people access to an object via i-Container, i-Container recognizes flow of the object and stores the logistical data as a permanent memory.
On the other hand when robots access to an object, robots need not to manipulate each object but need to handle i-Container. Such scheme may be easy and efficient for robots.
The system is composed of (A) a ceiling mobile container transfer robot, (B) a home-use automated container warehouse which realizes high space efficient storage and can collaborate with the container transfer robot and (C) iDock: an intermediate access point which is installed in our personal room (ex. Bed room, Child room).
By integrating these single function robots, we present a novel life style which can rescue us from over-flown objects and information.
intelligent Container (i-Container)

In our home-use logistical support robot system, an intelligent container (i-Container) plays a role of mediator between humans and robots, as a core technology of our system. So far, there were many researches and development about object manipulation, and thorough those effort we had acquired a lot of knowledge and know-how’s. Especially in industrial assembly application, fast and precise handling way achieved to realize high performance manufacturing system.
On the other hand, home robots must manipulate various objects comparing industrial application, and such flexible robotic manipulation is not easy in current robotics. Our goal is to realize a high efficient home-use storage/retrieval system, therefore the manipulation procedure is only one aspect of the whole system and not main topic. In our system i-Container is specialized in the fixing task and not only supports human to realize easy fixing but also supports robot to “support” human by their capabilities.
Concretely speaking i-Container can recognize contents of itself by reading RFID tags of the contents, make it easy for visual measurement system to acquire the position by blanking LED markers, and physically support the robot manipulation by guide structures.
In addition, i-Container has many variations. For storage use, 3 classes (S, A, E) are prepared to match the cost V.S. storage term problem, and compact refrigerator container, entertainment (DVD & writing desk) container and lavatory (Tooth brashing) container were developed for elder life support.
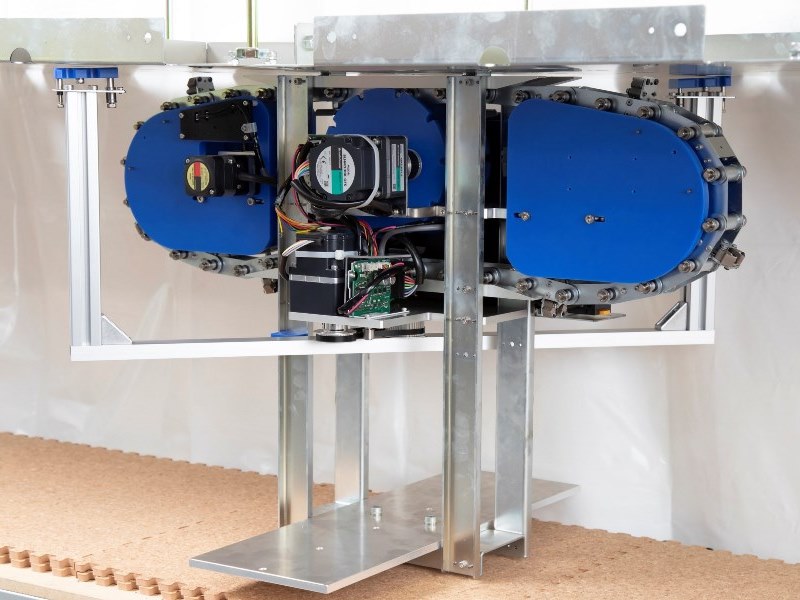
Container transfer robot

Container transfer robot was developed to realize a robust container transport motion without interference to humans in a living space. In general, there are many obstacles (daily-use object / furniture) on the floor of a living space. Therefore robots in the environment need to recognize the obstacles and plan their paths effectively. Especially in Japan, width of a corridor is small for human and robot to pass through simultaneously.
To solve the above problem, we present a novel and simple approach to utilize upper ceiling space as a main motion space of robots.
Additionally our living space has many disturbance factors for robots: ex. lighting condition, moving obstacles and residents themselves. To overcome the disturbance effect, the robot is implemented with some compliant (flexible) mechanisms. High stiff robot can realize precise and high speed motion but is not good at absorb some errors resulted from the environmental disturbance. Surely home robot should not injure the resident so the flexible mechanism can show good performance at reducing the accidental impact shock between human and the robot.
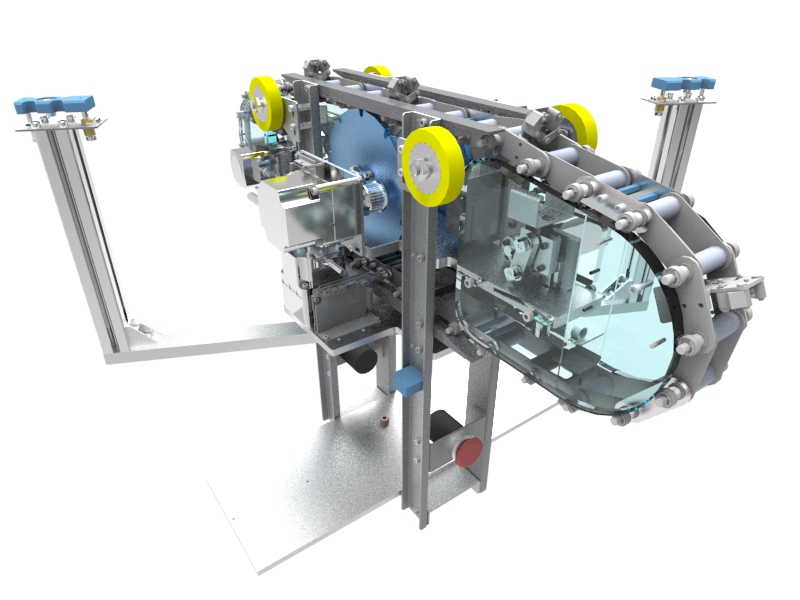
Home-use automated container storage/retrieval system

Home-use automated container storage/retrieval system (refer to s/r system) is an instrument to realize high space efficient storage of i-Containers and collaborative transport task with the Container transfer robot. An existing container warehouse requires a great deal of speed efficiency therefore users and the warehouse are separated by safety fences. But in home application a warehouse must cooperate with the users to keep the current living space and modern life style.
To achieve cooperative robot motion, horizontal and vertical motions of the s/r system are installed in a different body. To do so, the body size can be small and evacuation mode can be available by lifting the horizontal transporter up to ceiling.
Moreover it is not easy for the handling robot (horizontal transporter) to operate robustly i-Container which is placed by human. To achieve robust motion, a soft handling strategy; “caging” was introduced; therefore the robot can manipulate i-Container smoothly even placed by human without precise positioning.
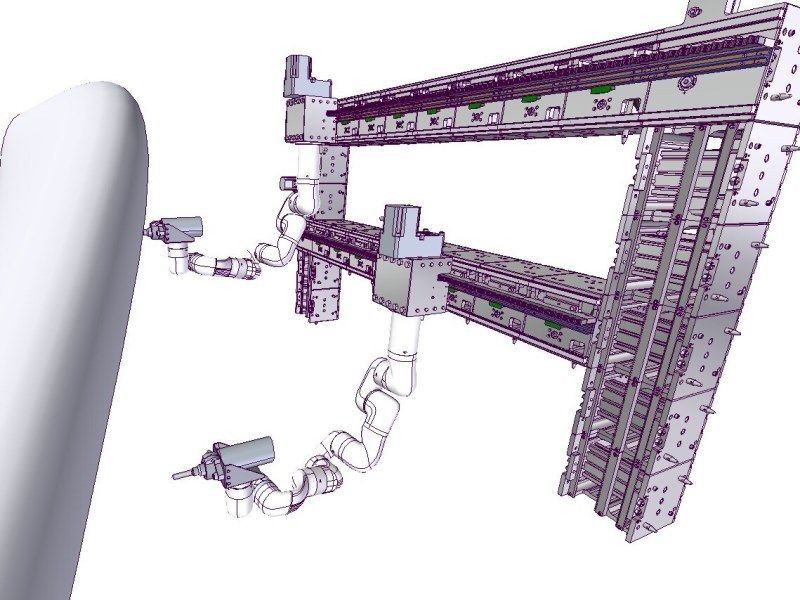
iDock: an intermediate instrument for home-use container logistics
“iDock” is an intermediate instrument which performs like an accesses point or hub in our home-use logistical support robot system. In general iDock is in compact mode not to invade the living space, but when necessary , its body and table are actuated to perform its capabilities.
When a user places i-Container on iDock, iDock recognizes the contents of i-Container by reading RFID tags and decides the storing place; ex. Upper ceiling storage or shelf type storage or not storing in storage. iDock has a guide plate to realize smooth i-Container delivery motion to the Container transfer robot. Thanks to the guide plate time efficiency and success rate of the delivery mission increases drastically.
Another feature of iDock is movable RFID antenna to recognize the contents of i-Container, the motion of antenna achieves robust RFID recognition despite of the position and posture of target RFID tags.
TansuBot : Object Search Supporting Instrument
“TansuBot” is a drawer type instrument to support daily-use small object search. Each drawer has a LED and an open/close detect switch. The switch acquires usage history. A wall moving robot in the back of the instrument has a portable camera to shoot the inside of drawers and has an extensive arm to realize pop-up function (pushing each drawer forward). By using the acquired information, users can search an object with a portable device such as a smart phone. In addition, the candidate of drawers that may contain the target object is emphasized by blinking LED and pop up action. These functions make the time short for searching an object. To keep the efficiency as storage, the space for moving robot is designed to be as small as possible. Considering the introduction of the instrument into a small store or a house, main parts are made of wood. They realize production cost reduction and user-friendly texture and appearance.
exStacker: A Non-Industrial Stacker Crane
Non-Industrial Stacker Crane enables humans to use high place for storage. Stacker crane is transport equipment carrying a container. In this research, we initially omit expensive sensors and actuators, and tried to develop an easily-installed stacker crane whose price is reasonable for home-use or small-shop-use.
The presented instrument has three features. (1) The instrument adopt a new storage system that makes containers deirectly hung on a wall. (2) A novel 2-DOF combined mechanism is composed of T-shape timing belt and two brakes. It realizes container lifting and inserting motions with only a single input handle. (3) The stacker crane can be easily extended into automatic mode just by adding electric and electronic components.
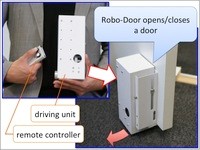
RoboDoor: A supplementary automatic door device
Robo-Door is an supplementary automatic door device by a wheel actuation. For home robots, door open/close is an essential but difficult task. Moreover, it is not practicable for robots without arms (ex. Roomba) to operate a door by themselves. Installing a door actuating device, the environment improves those robots' performances and promotes installation of current robot systems to living space. In addition, automatic open/close of a door is also helpful for humans with physical handicap, especially they use wheel chairs. Robo-Door selects a method of actuation by wheel. One advantage of actuation by wheel is simplicity of mechanisms Moreover, it could be installed to both a hinged and slide door, changing the direction of the device. In addition, Robo-door realizes an installation methodology without fabrication like a punch on a door, which is a Robo-Door's feature that other commercial products do not have.